Electrical Signaling in Living Cells: The First Image of a Potassium Ion Channel

MacKinnon, Roderick
Electrical signals underlie many of the body's essential physiological processes: they control the pace of the heart, blood pressure, and the secretion of hormones into the bloodstream, for example, and they transfer information in the nervous system. These signals are generated when ions such as sodium or potassium travel in or out of cells through one or more channels in the cell membrane. Since the 1950s scientists had techniques to measure and study this electrical activity. But Roderick MacKinnon (1956 - ) wanted to visualize how such channels work-and how a channel selects one type of ion and filters out others-by solving its atomic structure in three dimensions. Beginning in 1998, MacKinnon published a series of images that showed for the first time how electrical signaling occurs in a potassium ion channel. For this work he was awarded a Nobel Prize in 2003.
Like all ion channels, potassium ion channels each consist of a single protein molecule embedded in the cell membrane. To create an image of the molecule, MacKinnon first needed to purify a large quantity of the protein and get it to crystallize. Membrane proteins are notoriously difficult to crystallize and so MacKinnon had to devise ingenious methods to achieve this goal. Then, with the technique of x-ray crystallography, the diffraction pattern of x-rays beamed at the crystals could be translated into a computer generated image. MacKinnon's images explained two important features of the channel: how it allows potassium ions, which normally must be surrounded by water, to pass through the oily cell membrane, and how it discriminates between sodium and potassium ions, which are similar in size. His research also has clarified the chemical and voltage dependent mechanisms that control the opening and closing of the channels.
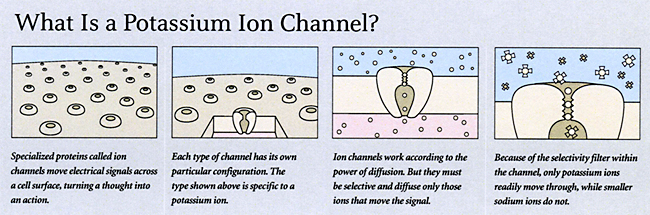
Diagram by Office of Communications and Public Affairs
MacKinnon received the BA in biochemistry from Brandeis University (1978) and the MD from Tufts University School of Medicine (1982). After medical residency at Beth Israel Hospital, Harvard Medical School (1982-1985) and postdoctoral work at Brandeis (1986-1989), he joined the faculty at Harvard Medical School in 1989. He moved to The Rockefeller University in 1996, where he is the John D. Rockefeller Professor. In addition to the Nobel Prize in Chemistry (2003), MacKinnon's work has been acknowledged with the Albert Lasker Basic Medical Research Award (1999), the Lewis S. Rosenstiel Award for Distinguished Work in Basic Medical Research (2000), the Gairdner Foundation International Award (2001), and the Louisa Gross Horwitz Prize (2003). MacKinnon is an elected member of the U.S. National Academy of Sciences (2000).
Selected Publications
Doyle DA, Cabral JM, Pfuetzner RA, Kuo A, Gulbis JM, Cohen SL, Chait BT, and MacKinnon R. The structure of the potassium channel: molecular basis of K+ conduction and selectivity. Science, 1998, 280: 69-77
Jiang YX, Lee A, Chen JY, Cadene M, Chait BT, and MacKinnon R. Crystal structure and mechanism of a calcium-gated potassium channel. Nature, 2002, 417: 515-522
Jiang YX, Lee A, Chen JY, Cadene M, Chait BT, and MacKinnon R. The open pore conformation of potassium channels. Nature, 2002, 417: 523-526
Jiang YX, Lee A, Chen JY, Ruta V, Cadene M, Chait BT, and MacKinnon R. X-ray structure of a voltage-dependent K+ channel. Nature, 2003, 423 :33-41
Ruta V, Jiang YX, Lee A, Chen JY, and MacKinnon R. Functional analysis of an archaebacterial voltage-dependent K+ channel. Nature, 2003, 422: 180-185
Long SB, Campbell EB, and MacKinnon R. Crystal structure of a mammalian voltage-dependent Shaker family K+ channel. Science, 2005, 309: 897-903
Schmidt D, Jiang QX, and MacKinnon R. Phospholipids and the origin of cationic gating charges in voltage sensors. Nature, 2006, 444: 775-779
Long SB, Tao X, Campbell EB, MacKinnon R. Atomic structure of a voltage-dependent K+ channel in a lipid membrane-like environment. Nature, 2007, 450: 376-NIL_3
Links
Laboratory of Molecular Neurobiology and Biophysics at Rockefeller University
http://www.rockefeller.edu/labheads/mackinnon/mackinn-lab.php
The Nobel Prize in Chemistry, 2003
http://nobelprize.org/nobel_prizes/chemistry/laureates/2003/index.html
Albert Lasker Basic Medical Research Award, 1999
http://www.laskerfoundation.org/awards/1999basic.htm
HHMI Research Abstract: Structure and Mechanism of Ion Channels
http://www.hhmi.org/research/investigators/mackinnon.html
How Our Bodies Turn Thought Into Action
http://www.rockefeller.edu/interactive/mackinnon/ion_channel.html
Ion Channels for Beginners
http://opal.msu.montana.edu/cftr/IonChannelPrimers/beginners.htm
Hodgkin and Huxley's Model of an Action Potential
http://physioweb.med.uvm.edu/cardiacep/EP/handh.htm